Customer Lifetime Value
| What you put in... | What you get out... |
|
|
Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) is a metric of a customer's value to the organization over the entire history of the relationship. Short-term sales are a factor, but so are overall customer satisfaction, the churn rate in the segment, and the costs to acquire a new customer and retain an existing customer.
 The model uses the following input:
The model uses the following input:
Segment Description
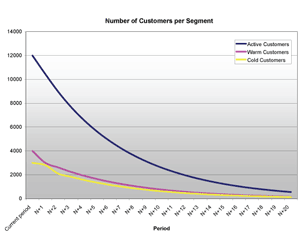
- Number of Customers per segment. As of today, how many customers does the company have in each segment?
- Gross Margins are the average margins that can be expected from a customer over each period (e.g., a year, a quarter), based on which segment this customer belongs to at the beginning of this period.
- Marketing Costs quantifies how much money the company spends per customer and per period, depending on which segment this customer belongs. Typically, active customers are followed more closely, receive more attention (e.g., direct marketing solicitations or sales representatives visits), and cost more to the firm.
Transition Matrix
- The Transition Matrix summarizes the likelihood a customer will switch segments at each period. This matrix should be read horizontally, and each line sums up to 100% (since all customers need to go somewhere). In the above example, an "active customer" has a 75% likelihood of still being in the same segment next period, and 25% chance of switching to the "warm customer" segment.